Table of Contents
How Germs Spread in Food and How to Deal with Them
Germs often settle on meat, fish, eggs, lettuce and are an invisible danger: Depending on the type and quantity, germs spread in food can make you sick and even be life-threatening. We introduce the most common pathogens and give tips on how to protect yourself against infections.
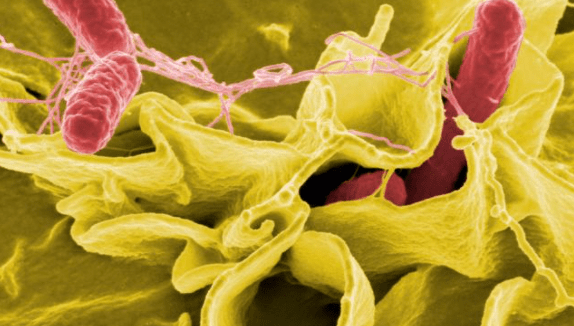
#1 Salmonella
Salmonella belongs to the enterobacteria family and colonizes the intestines of animals, especially pigs and chickens.
They can contaminate eggshells through excretions and, in meat processing, also beef and chicken. The pathogens also survive freezing temperatures, which is why they can be found in the thawing water of frozen poultry and other meat.
An infection with the bacteria can cause diarrhea, headache, fever, and vomiting for several days. In babies, toddlers, and the elderly, severe courses are also possible, which in the worst case can lead to death.
How you can protect yourself: Several good practices could be used, and the best one is to eradicate any presence of Salmonella by using appropriate and high effective disinfectants:
- Rinsing or spraying on raw meat with a natural disinfectant like ECOLYTE MEAT AND SEAFOOD DISINFECTANT keeps you protected.
- Frequently spray this specially made disinfectant, which will instantly kill and neutralize 99.995 % of the germs inside your refrigerator, and don’t forget trays and inside corners. Doing this will keep you out of this tiny bacterium.
- Kitchen utensils and work surfaces should be cleaned immediately and rinsed or sprayed with the same ECOLYTE MEAT AND SEAFOOD DISINFECTANT after getting into contact with raw eggs, raw meat, and defrosted water.
Additionally, thaw unpackaged frozen food in a covered bowl in the refrigerator. children, the sick ones, and elders should only eat thoroughly heated egg dishes.
The following applies to dishes with raw eggs such as tiramisu or homemade mayonnaise: only use fresh, undamaged eggs, cool quickly, and, if possible, consume immediately.
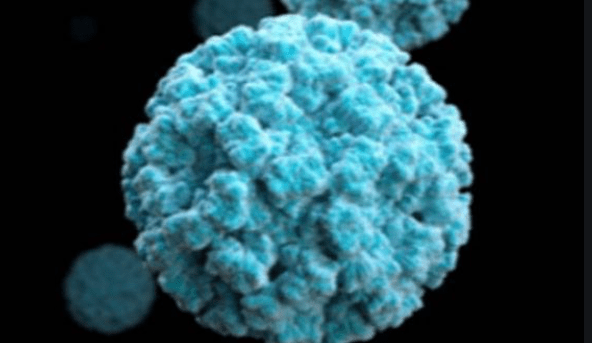
#2 Noroviruses
Noroviruses are mainly transmitted through contact with sick people or dirty surfaces. But food can also cause infections.
Salads, frozen berries, and raw vegetables have all been implicated in norovirus outbreaks. In principle, however, all foods prepared under poor hygienic conditions and not sufficiently heated can be affected.
Mussels can accumulate noroviruses from the water and make them sick if they are eaten raw.
Noroviruses are responsible for most gastrointestinal infections that are not caused by bacteria. The diseases occur particularly frequently in winter.
Typical symptoms are violent, gushing, vomiting, nausea, abdominal cramps, and severe diarrhea. The symptoms usually go away after three days. The disease can become threatening for children, older people, and immunocompromised patients. Noroviruses are often the cause of disease outbreaks in community facilities, older people’s homes, hospitals, or cruise ships.
How you can protect yourself: Whatever salads, seasonal fruits, or mussels, the most effective solution would be:
- It is advisable to rinse or soak your vegetables and fruits with a disinfectant spray like the ECOLYTE FRUITS AND vegetable DISINFECTANT. This powerful 100% natural food sanitizer spray eradicates and kills 99.995% of germs such as Noroviruses in seconds.
- Similarly, keeping mussels or your seafood for about 15 seconds in such a sanitizer and disinfectant will neutralize any norovirus, all germs, and pathogens.
- Moreover, adopting proper hygienic habits like washing hands with soap after using the toilet or before eating will be a plus and reduce the risk of infection. And it’s also essential to the point that sick people should not prepare food for others. And proper heating tends to make the pathogens harmless.
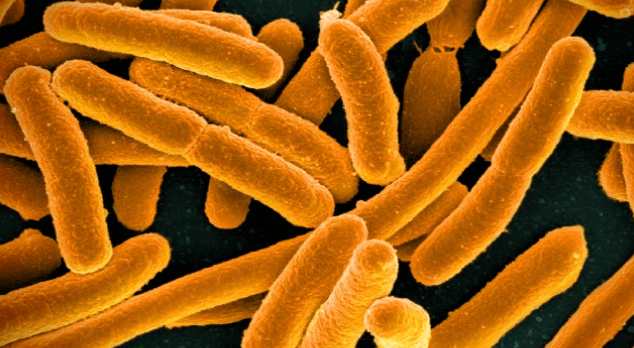
#3 Escherichia (E.) coli
These representatives of the enterobacteria settle in the digestive tract of warm-blooded mammals. For example, when processing cattle, the bacteria can get from the animal intestines onto the meat and products made from it, such as minced meat or salami.
Drinking water can also be contaminated with germs, through which they can get on sprouts and raw vegetables.
Escherichia coli is one of the most common pathogens for bacterial urinary tract and gastrointestinal infections, wound and respiratory tract infections worldwide.
The germ is also notorious as a cause of blood poisoning and hospital infections. Some strains can cause meningitis in newborns. Children and the elderly or people with a weak immune system are particularly susceptible to infection.
How you can protect yourself: keep in mind that only highly effective and nontoxic disinfectants will provide valuable solutions and tackle the Escherichia coli:
- Their proper use during the meat processing or to clean our kitchen is essential. You’re advised to rinse or soak any of your meat for seconds in a dedicated Hypochlorous acid disinfectant to prevent contamination. The same with your other fresh garden food for which a wash or soak in a veggie clean is greatly advised.
- Additionally, proper cooking and heating of the meat will be a plus and will kill germs.
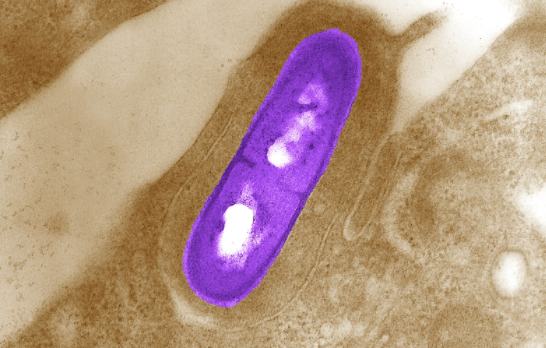
#4 Listeria
The pathogens occur in the soil, on plants, in compost, and in sewage. Listeria is also widespread in agriculture so that they can also spread to vegetables via the earth.
If the hygiene measures are not observed in companies, the bacteria can also find their way into preserved and processed foods. Frequently affected foods are raw milk, cheese, smoked fish, and raw meat such as fresh chicken thighs.
Listeria can lead to what is known as listeriosis in humans. In healthy people, an infection often manifests itself as brief, febrile diarrhea.
In pregnant women, the elderly, or people with a weak immune system, listeriosis can also cause blood poisoning, encephalitis, or meningitis and even be fatal. Pregnant women are at risk of premature births and stillbirths.
How you can protect yourself: Unfortunately, it’s true to say that chilling or freezing your food is not enough:
- Sensitive people should avoid eating raw animal foods such as raw milk, cheese, and raw sausage or smoked and marinated fish products unless been sure to use dedicated products to wash fresh fruits and vegetables, also meat, seafood, or lettuce and peel varieties that grow close to the ground, such as carrots or cucumbers.
- Also, it’s a must always to pay great attention to kitchen and house hygiene and use solutions like ECOLYTE MULTI-SURFACE DISINFECTANT, the powerful and odor removal surface cleaner and sanitizer that will keep you out of risks.
- Alternatively, proper cooking, roasting and pasteurizing tend to kill Listeria, and the core of the food must be heated through, at minimum 70 degrees Celsius for at least two minutes.
#5 Antibiotic-resistant germs
Antibiotic-resistant germs are bacteria that are insensitive to certain antibiotics. Well-known representatives are MRSA (methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus) and ESBL-forming germs (extended-spectrum beta-lactamases).
They can often be found in meat and chicken thighs. Sometimes, massive use of antibiotics in animal fattening means that resistant germs develop and spread.
However, animals that have never received an antibiotic can also be colonized. Because the germs spread and can survive cleaning and disinfection measures, a small number of them is enough to infect freshly housed chickens. In addition, resistant pathogens can reach previously unpolluted meat in the slaughterhouse.
Many ESBL-producing bacteria often do not make you sick themselves. However, they can transfer their resistance genes to more dangerous pathogens.
How Germs Spread in Food and 4 solution to Deal with Them Share on X
If people get them, certain antibiotics may fail. The disease can then be more severe and, in the worst case, even lead to death.
MRSA is rarely passed on through food. They are often found on meat, but only in small quantities. However, if a large MRSA penetrates a wound, there is a risk of serious infections, which are difficult to treat.
The germs that can develop the ability to form ESBL include Salmonella or EHEC. They can cause the same symptoms as non-resistant bacteria of these types, for example, diarrhea.
How you can protect yourself: Anyone who has had contact with animals should wash their hands with warm water and soap. Otherwise, it helps to follow the relevant hygiene rules:
- Cook eggs and meat well before eating. And a prior food washing is highly recommended (best with Ecolyte).
- Wash lettuce, fruit, and vegetables thoroughly.
- Finally, wash your hands before and after preparing raw meat.
#6 Campylobacter
Campylobacter is the most common cause of bacterial food infections: The Robert Koch Institute (RKI) registered around 62,000 cases of illness connected with the germ in 2019.
It colonizes the intestines of animals, especially poultry. It often ends up on meat in slaughterhouses. According to the Federal Office for Consumer Protection and Food Safety, Campylobacter bacteria were detectable in almost every second sample of fresh chicken in 2019.
Just a few pathogens are enough for an infection. They can also be transmitted through contact with an infected animal and humans.
Campylobacter can cause gastrointestinal infections with diarrhea, abdominal pain, and fever. Usually, the symptoms are overcome after a few days.
However, there is a higher risk of severe disease progression in young children, pregnant women, the sick, and the elderly. The bacterium causes joint inflammation and Guillain-Barré syndrome in rare cases – a nerve disease associated with paralysis.
Typically, muscle pain and headache with fever occur first, followed by diarrhea, vomiting, and severe abdominal pain. These complaints can appear immediately after consumption but also after around eight days. Children under five years of age and young adults between 20 and 29 are often affected by Germany’s illness. Infections are widespread in the warm season. If you suspect a Campylobacter infection, you should see a doctor immediately.
How you can protect yourself: As said above, engaging yourself in good prevention practices is the key to avoid Campylobacter contamination:
- Rinsing or use of safe sanitizer spay on raw meat will kill all the germs.
- Their use inside your refrigerator, trays, kitchen, various utensils, and work surfaces is the perfect solution to end the problem.
- Keep in mind that splashing water increases the risk of any germs spread in the kitchen. Risk groups such as children, immunocompromised people, and pregnant women should avoid raw meat and unpasteurized dairy products such as raw milk cheese unless to be sure that these foods are entirely disinfected or cooked the right way.
#7 Ehec (Enterohemorrhagic E. coli)
The Ehec bacteria belong to the Escherichia (E.) coli family, more precisely to the E. coli group, producing Shiga toxins. Shiga toxin-producing E. coli (abbreviated: Stec) is sometimes called verotoxin-producing E. coli (Vtec for short). Those of these germs that cause disease in humans are known as enterohaemorrhagic E. coli (Ehec).
Ehec is found in the intestines of ruminants such as cattle and sheep. They find their way into the environment through the excrement and into meat products through processing. Evidence of Ehec in food is usually indicative of fecal contamination. The pathogens are mainly found in raw or insufficiently heated foods, such as raw milk products, raw sausages such as tea sausages, and raw or insufficiently heated meat. Ehec can also get on plant-based foods such as sprouts through contaminated water. The germs spread into the grain through manure and wild ruminants (such as deer).
In the United States and Canada, Ehec in flour has caused disease outbreaks in recent years. The Ehec pathogen can cause severe, sometimes bloody diarrhea. Infection can trigger hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS), especially in young children. This can lead to acute kidney failure, bleeding disorders, and the destruction of red blood cells with possible fatal outcomes.
How you can protect yourself: The germ survives cooling in the refrigerator and freezing. However, it is killed by intense heat during cooking, frying, and baking, even if we all could imagine how bad an intense heat will lead to our food nutrients. And the best options are:
- Rinse or soak any vegetables and fruits before consuming them.
- Similarly, keeping meat and seafood for about 10-15 seconds in a low concentrate HOCL will neutralize the pathogens.
- Moreover, researchers recommend that raw animal foods and flour be particularly hygienic, and no one should snack on raw dough. Also, risk groups should avoid untreated sprouts, raw milk products, and spreadable raw sausages such as tea sausage.
#8 Mold toxins
Mold can attack grain in the field. In addition, their spores find their way into food through the air.
Once there, they form nests that quickly enlarge in a warm and humid climate. Molds mainly affect cereals, dried fruits, pistachios, nuts, corn kernels, spices, bread, and rolls. Their mesh can pull the food through even where no infestation is visible.
Some molds produce carcinogenic toxins, for example, aflatoxins. These can damage the kidneys, liver, and the unborn child in particular. In addition, the genetic material can be damaged.
How you can protect yourself: Store perishable food in a cool place with as little air as possible. However, heat cannot harm the toxins.
Food with moldy areas should be thrown away as completely as possible – even if only small areas of mold are visible. Other foods such as nuts or spices are not infested.
Discard anything that smells or tastes bitter, musty, and rancid. Overlaid nuts and spices also belong in the trash. And let our various eco sanitizers do the job for you by removing any mold and odor.
How to Stop Germs Spread in Your Kitchen
#1 Refrigerator
Some germs, such as Listeria, even multiply at refrigerator temperature. The invisible pathogens particularly like to romp around in the vegetable drawer and the drainage channel on the rear wall of the refrigerator.
Open food in the refrigerator should therefore be covered. Do not overfill the refrigerator.
The air must circulate. And as we read earlier, it is also highly recommended to wipe, spray and wash the refrigerator regularly with nontoxic disinfectants.
#2 Avoid dishcloths and sponges
Numerous pathogens multiply very well in dishcloths and sponges soaked in food residues and moisture, which quickly become germs.
Every time you wipe the table and work surface, germs spread onto the supposedly cleaned surface. Therefore, sponges and rags should be replaced frequently and soaked in our home sanitizer solution. Additionally, always wash and rinse the kitchen cloth thoroughly and spread it out to dry.
#3 Clean cutting boards
To avoid cross-contamination, boards and knives should be cleaned with special washing-up liquid after contact with raw food. Once well cleaned, they do not pose a greater hygiene risk than other utensils.
Cutting boards with deep cracks – whether made of plastic or wood – are not recommended to use. Germs can survive just fine in the cracks if they don’t come in contact with a powerful disinfectant.
#4 Wash Hands
It should go without saying that you should wash your hands with soap before and after preparing food, especially after using toilets. The same applies after sneezing and blowing your nose.
Also important to stop Germs Spread: Always wear clean clothes, tied up hair, have no rings while cooking, apply plaster to cover any wound on the finger, and never keep your kitchen and house out of ECOLYTE 100% natural disinfectants. Say no to GERMS!
Do you know, Little Negligence Can Cause Big Problems?
Washing with cold or warm or saltwater won’t get rid of all the germs. Switch to Ecolyte+, 80x more powerful than most conventional cleaning.
Ecolyte is 100% natural and safe, hypoallergenic, effective in killing 99.99% of germs & having no side effects on kids, pregnant women, Senior Citizens, plants, pets, and even marine life.
Ecolyte is fully integrated and certified having ISO 9001:2015 ( Quality Management System), ISO 22716:2007 (Good Manufacturing Practice), ISO 45001:2018 (Occupational Health & Safety Management Systems), ISO 14001:2015 (Environmental Management Systems), and all the materials that we use are considered completely safe as raw materials for our products.
Ecolyte products have been approved by the Federal Government through the Emirates Authority for Standardization and Metrology (ESMA) & Dubai Municipality (DM).
Try Ecolyte+ disinfectant products through our Online STORE
Product is also available at all major online platforms & Hypermarkets in UAE.